Find out how cybercriminals are using Hugging Face to spread thousands of Android malware variants. Learn all about the TrustBastion, campaign, polymorphic malware, and how you can protect your Android device.
Trust Under Fire: How Hackers Are Using Hugging Face to Spread Android Malware
In the highly dynamic world of Artificial Intelligence, platforms like Hugging Face are playing an essential role. In most instances, developers are flocking to these platforms, sharing machine learning models. The trusted reputation of these platforms is being exploited by cybercriminals. In this respect, the platforms are being used to spread sophisticated Android malware. In this way, the ongoing Android security saga is being taken to the next level.
Recent studies carried out by security researchers have revealed that cybercriminals are using the Hugging Face platform to spread malware. The use of the platform is being done in such a manner that the inherent trust associated with the platform is being exploited. In this respect, the platform is being used to spread thousands of Android malware variants.
The Unsettling Abuse of a Trusted AI Platform
Hugging Face is generally accepted as a legitimate and vital tool for the AI community. The main function of this website is to host different AI models, datasets, and development tools. It is this perception of legitimacy, which attackers are taking advantage of. Attackers are hosting their malicious payloads on this website, thereby giving them a cloak of legitimacy. This means that these downloads are not easily flagged by malware detection tools, thereby making it easy for malware to spread.
Although this misuse of trust is not brand-new, the recent Android campaign’s scope is especially concerning. The attackers are doing more than just hosting a few malicious static files. Rather, they are operating in a very dynamic manner. To avoid detection, for instance, they upload new malware variants on a regular basis. This clever tactic shows a thorough comprehension of both platform mechanics and current security flaws. As a result, it presents a significant obstacle to conventional threat detection techniques, requiring more flexible defenses.
TrustBastion
> Android Malware Analysis Platform
TrustBastion: A Deceptive Entry Point
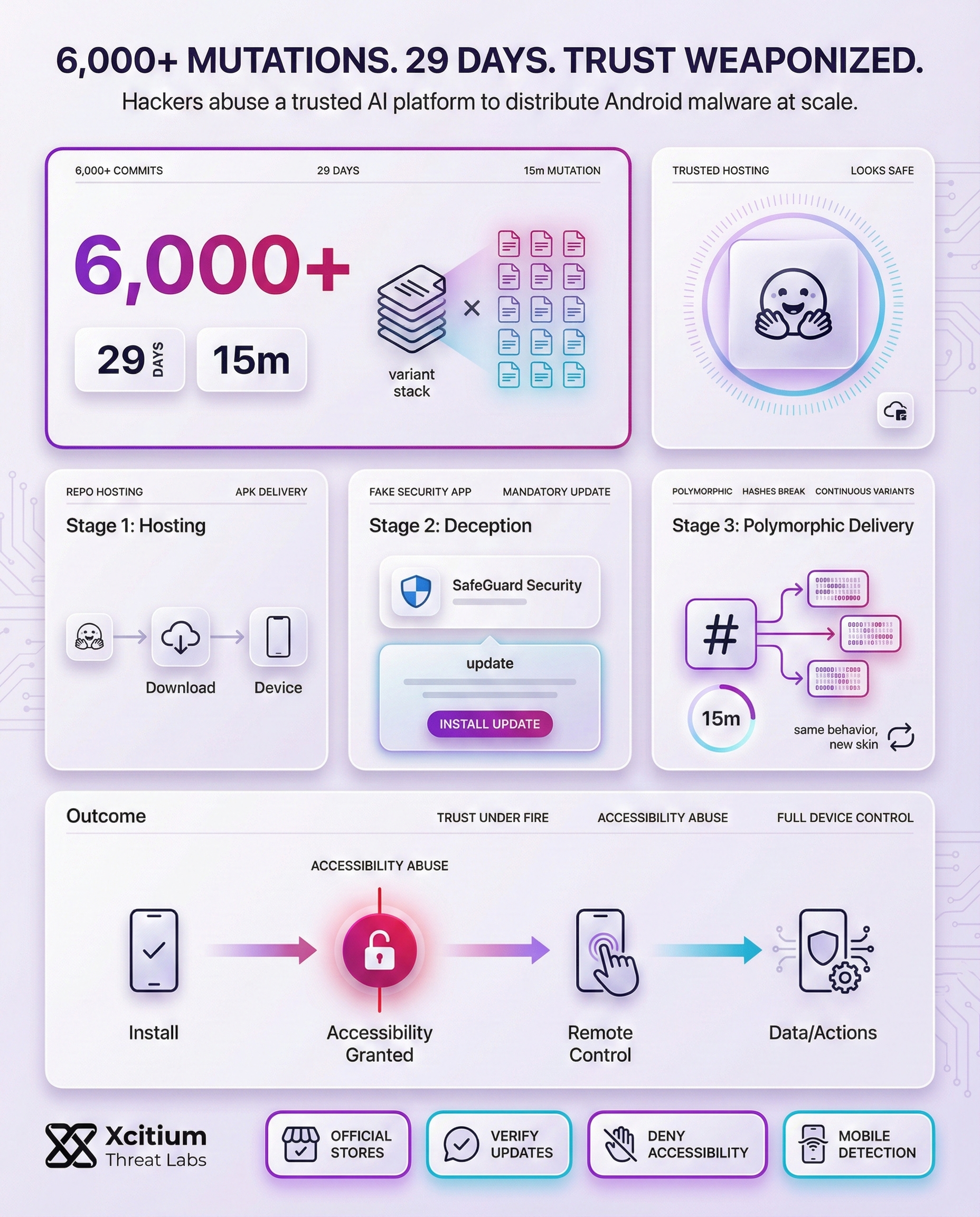
Usually, the attack starts with a malicious program named “TrustBastion.” This app is cleverly marketed as a security tool, claiming to shield users from phishing, scams, and other mobile dangers. Actually, it is the first dropper for the next malware payload. Using traditional scareware techniques, the app deceitfully warns users that their device is seriously compromised. It then starts the malicious download process by asking them to do a “mandatory update” to fix these imaginary problems.
This update procedure is deftly disguised to look authentic. The app successfully lulls users into a false sense of security by presenting an interface that closely resembles the well-known Google Play Store. However, the dropper communicates with its command-and-control server rather than providing an actual update. A redirect link to a Hugging Face-hosted repository is then provided by this server. The last malicious payload is then downloaded and installed. Under the pretense of a regular security update, all of this happens smoothly.
The Polymorphic Threat: Evading Detection
This campaign’s creative use of server-side polymorphism is among its most advanced features. This sophisticated method enables the attackers to produce and upload new malware payload variants automatically and remarkably frequently. According to reports, a new version was made in this particular instance roughly every fifteen minutes. Researchers saw more than 6,000 distinct commits to the malicious repository over the course of a 29-day investigation. The malware is a constantly shifting target due to its quick mutation, which greatly complicates detection efforts.
Furthermore, this high degree of polymorphism is intended to thwart conventional antivirus software. Hash-based detection, which recognizes malware by its distinct digital fingerprint, is the main method used by many security tools. These traditional detection techniques are essentially useless since every new variant has a unique hash. Although the malware’s signature is constantly changing, its fundamental behavior stays constant. This makes it necessary for security systems to use increasingly sophisticated machine learning and behavioral analysis methods in order to correctly detect the changing threat.
Attackers utilize automated generation to upload new malware variants, creating a constantly moving target for security systems.
During a 29-day investigation, over 6,000 unique commits were observed in the malicious repository.
Traditional AV tools relying on hash-based detection are rendered ineffective as every variant possesses a unique signature.
While core behavior remains consistent, the signature changes constantly. This forces a shift from static analysis to behavioral AI and machine learning for accurate identification.
Unmasking the Remote Access Trojan (RAT) Capabilities
After its successful installation, the payload works as an extremely powerful RAT. The initial action it undertakes is to demand access to the Android device’s Accessibility Services. The malware cleverly presents this as a security measure, hence allowing it to gain access to a plethora of permissions. This, in turn, offers it immense power over the infected device. This includes, but is not limited to, closely monitoring all activities carried out on the device, capturing screen content, and even making on-screen gestures, without seeking any kind of approval from the victim.
The RAT utilizes its immense capabilities for a number of malicious activities, such as:
- Credential Theft: The RAT presents false login prompts for commonly used financial and payment-related applications, like Alipay and WeChat, with the primary intention of stealing critical user credentials.
- Screen Lock Interception: The RAT goes one step further by actively seeking to intercept the PIN or password used for locking the screen, which would potentially offer hackers complete, unhindered access.
- Persistence: Perhaps most critically, it actively works towards blocking any attempt made by the victim/user to uninstall the malicious application, hence offering it complete, unhindered access.
Safeguarding Your Android Device: Essential Precautions
Considering the fact that threats like the TrustBastion attack have become more and more complex, it has become more important for the end-user to be vigilant than it has ever been. Although Google Play Protect provides a level of security through the scanning of applications for known threats, it has become imperative for end-users to take proactive steps towards ensuring the security of their device from such stealthy attacks. In this regard, it has become important for end-users to develop some key security habits that can help them protect their device from such attacks.
To begin with, it has become imperative for end-users to never download applications from third-party app stores or websites. It has become important for end-users to always use the official Google Play Store for downloading applications, as it has become more secure than other app stores. It has also become important for end-users to always scrutinize the permissions that an application requires when it is being installed on the device. It has become important for end-users to be wary if an application requires access permissions for the device’s accessibility services.
Conclusion: When Trusted Platforms Become Malware Delivery Networks
The Hugging Face abuse behind TrustBastion proves a modern Android reality, attackers no longer need shady infrastructure. They borrow legitimacy from reputable platforms, then hide the payload behind a fake security narrative and a familiar update flow. Once a user grants Accessibility access, the attacker can watch, click, steal credentials, intercept screen locks, and block removal.
Why This Threat Scales So Fast
This campaign succeeds because it blends into normal behavior, and traditional indicators fail to stand out.
- Legitimate cloud hosting makes downloads look safe
- Rapid polymorphism breaks hash-based detection, new variants appear continuously
- The “security update” story drives users to self-install, then self-authorize the compromise
- Accessibility permissions turn one mistake into full device control
Where Xcitium Breaks the Attack
With Xcitium Cyber Awareness Education and Phishing Simulation, this attack would not succeed, because the decision point is trained before the scan.
- Users learn to distrust urgent “mandatory update” prompts outside official stores
- Simulated campaigns build pause and verify habits before credentials are entered
- High-risk permission requests, especially Accessibility, are treated as a stop signal
- The attacker loses leverage when the user never completes the install and permission steps
Protect Android Trust Paths Before They Are Weaponized
When criminals can weaponize a trusted AI platform to distribute thousands of mobile variants, defense starts with behavior. Reduce risky installs, deny dangerous permissions, and build user instincts that stop the chain early.




